Diamond Education
So why us? Why Gemaxis Jewellery?
Gemaxis is very passioned about Jewellery and making people feel on top of the world when they receive their piece of handmade Jewellery. Gemaxis will source you the highest quality Diamonds to suit your budget.
We are dedicated to create something beautiful, which will last for years to come. Therefor we must use the highest quality ‘ingredients’ available to ensure we reach this goal. Why make a beautiful ring with dull looking Diamonds?
Our in-house Gemmologist will guide you through the process of selecting the right diamond for your budget. Gemaxis’ network stretches worldwide, with reputable and certified gemstone merchants sourcing the most desirable stones available to suit your budget. We will find that ‘Sweet Spot’ where beauty and value meet, without making a compromise.
Depending on personal preferences, we don’t compromise on the Cut of the diamond, whereas with other areas we have more flexibility, which won’t influence the beauty of the diamond with the naked eye.
However, here at Gemaxis we rather use Diamonds F colour or above in our pieces and depending on the Carat, and only Diamonds Si or above in Clarity. This is how we ensure that you are getting the best value for money and therefor a beautiful eye-clean sparkling Diamond in a designer piece of Jewellery.
The Gemaxis 5 C’s
Diamond Cut
Diamond Cut is how well a diamond is cut and polished, including how well-proportioned the stone is, its depth and symmetry. Diamond Cut doesn’t refer to the shape of the diamond, such as an Oval or Pear Shape. Cut quality directly impacts the diamond’s beauty and brilliance. A well cut diamond is luminous and reflects white and coloured light back to your eyes. At Gemaxis Jewellery we only source diamonds with an Excellent or Very Good cut, anything below is be considered inferior to work with. Unlike any of the other 4 C’s (being Clarity, Colour & Carat), Diamond Cut is the one we rather don’t compromise on, as there is no hiding a below-average cut. Even if your budget forces you to sacrifice in other areas, a well-cut diamond should still have the potential to stand out.
The amount of light return and brilliance found in an exceptionally cut diamond is worth the extra diamond cut price. Without brilliance and fire, a diamond is less than radiant, no matter the Carat weight or table size.
GIA diamond cutting grades for round diamonds range from Excellent to Poor. Diamond cut grade is based on a number of factors including symmetry, polish, brilliance and fire. For the most brilliance and beauty, only consider round brilliant diamonds with an Excellent or Very Good cut.
GIA Cut Scale
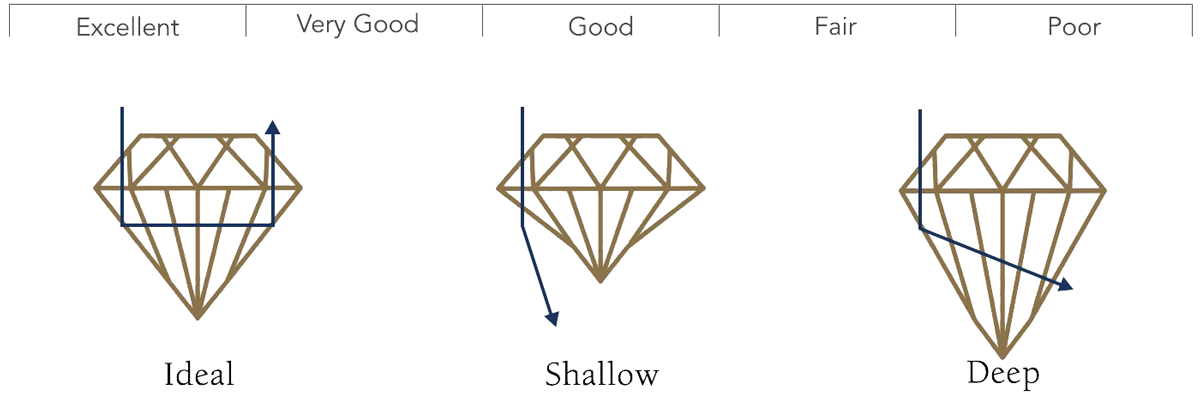
Diamond Cut Grade
| Excellent | Excellent Cut Diamonds provide the highest level of fire and brilliance. Because almost all of the incoming light is reflected through the table, the diamond radiates with magnificent sparkle. |
| Very Good | Very Good Cut Diamonds offer exceptional brilliance and fire. A large majority of the entering light reflects through the diamond’s table. To the naked eye, Very Good diamonds provide similar sparkle to those of Excellent grade. |
| Good | Good Cut Diamonds showcase brilliance and sparkle, with much of the light reflecting through the table to the viewer’s eye. These diamonds provide beauty at a lower price point. |
| Fair | Fair Cut Diamonds offer little brilliance, as light easily exits through the bottom and sides of the diamond. Diamonds of a Fair Cut may be a satisfactory choice for smaller carats and those acting as side stones. |
| Poor | Poor Cut Diamonds yield nearly no sparkle, brilliance or fire. Entering light escapes from the sides and bottom of the diamond. |
Diamond Pricing Factors
Here are the main factors that affect the price of a diamond:
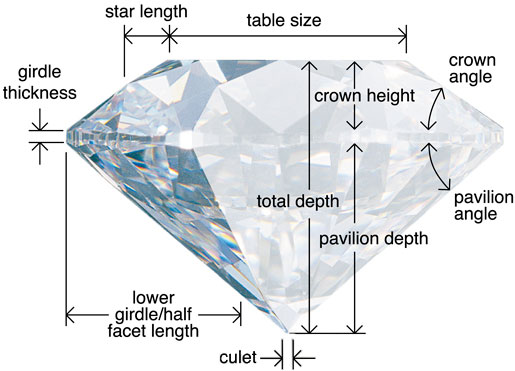
Proportions (table, width, depth)
Symmetrical facets (the mirrors, windows and steps of a diamond)
Brilliance (brightness of white light reflection)
Fire (dispersion of coloured light)
Scintillation (the flashes of sparkle when light moves)
Finishing details (permanent treatment and polishing)
Brilliance
A diamond’s brilliance is the brightness of the white light reflection. When looking at a diamond face-up under light, it should reflect an abundance of white light. A diamond that’s not symmetrical, is cut too deep or too shallow, for example, looks dull instead of brilliant.
Fire
A diamond’s fire is the amount of coloured light that reflects off the table and facets. Diamonds that are well cut not only have brilliance but fire too. When looking at the diamond face-up under light—especially daylight—you should see coloured light bouncing off the diamond. If the diamond doesn’t exhibit coloured light reflection, the diamond has a low amount of fire.
Scintillation
Scintillation of a diamond refers to the flashes of sparkle when light moves on the diamond’s table and facets. The scattering of light resembles a sparkle and is caused by the light and dark areas on the diamond’s surface. A diamond with a large amount of scintillation is more desirable. A diamond without much scintillation can appear dull.
Finishing details
The finishing details are the craftsmanship of the diamond and include its permanent treatment and polishing. The polish of a diamond refers to the condition and quality of the facet surfaces. A diamond that is polished well creates a clear mirror for light to reflect off. A diamond with a poor polish job looks dull because the facets don’t reflect light as vividly.
Because Diamond Cut is an enormous element in determining the beauty and brilliance of any diamond, there are some complexities. Many factors play a role in how a diamond’s cut quality is determined.
The main factors impacting Diamond Cut Quality are:
Proportions: the ratios and sizes of the diamond’s depth, width and table
Symmetry: precision of the facets, mirrors, windows and steps
Polish: the shine and glow of the diamond surface
Colour
As diamonds come from the ground, they usually have yellow, brown, or grey colours because of the impurities they pick up in the earth. These diamonds are rated based on hue, tone, and saturation, and the diamond colour scale includes those factors.
Diamond hue includes the stone’s actual colour – for example, white, yellow, pink, brown, or blue. A gem’s tone is the degree of colour, from light to dark. Finally, saturation is the colour’s depth and intensity. Colourless diamonds do not have saturation. Instead, they have fire and brilliance.
The Gemmological Institute of America (GIA) developed the International Colour Scale to bring consistency in labelling diamond colour. This scale addresses colour and clarity with a jury system that evaluates every diamond. The five-person jury must unanimously agree on the grade for the diamond to receive GIA certification.
The official GIA scale measures the colour hue in white diamonds using letters ranging from D to Z to measure the degree of yellow, brown, or grey in a stone. To showcase colour flaws, gemmologists evaluate the colour by placing diamonds face down on pure white paper. Diamonds with a D rating must be icy white and colourless, while those with a Z rating have a yellow hue. Gemaxis Jewellery will normally only use D, E & F colour diamonds in our Jewellery, however in some cases we may use a G, H, I & J colour Diamonds, due to personal preference.
Diamonds that earn a D, E, or F grade are totally colourless. Only an electric colourimeter would distinguish the subtle differences. Customers cannot tell the differences between the three colourless grades, as none of them have any distracting or unwanted yellow or brown hues. The prices on colourless diamonds are relatively similar, regardless of the D, E, or F grade.
Near colourless diamonds are graded between G and J. They have a warmth to them, but any colour is difficult to see unless they are next to colourless diamonds. The G diamond is one of the most popular near colourless grades because it has the least amount of colour and is inexpensive when compared to colourless options.

GIA Colour Grade Scale
|
D |
Absolutely colourless or icy white. The highest colour grade—extremely rare and most expensive. |
|
E |
Colourless. Only miniscule traces of colour can be detected by an expert gemmologist—a rare, high-quality diamond. |
|
F |
Colourless. Slight colour detected by an expert gemmologist, but still considered a “colourless” grade—a high-quality diamond. |
|
G |
Near colourless. Colour noticeable when compared to diamonds of better grades. |
|
H |
Near colourless. Colour noticeable when compared to diamonds of better grades. |
|
I |
Near colourless. Slightly detected colour. |
|
J |
Near colourless. Slightly detected colour. |
Clarity
Diamond clarity refers to the purity and rarity of the stone, and the degree to which it presents blemishes and inclusions. When forming, natural microscopic characteristics can be trapped within or on the diamond. These internal and surface characteristics are inspected by gemmologists, who use 10x magnification and a qualitative grading system to assign a numerical value (clarity grade) to each diamond.
The lower the number of imperfections and flaws in a diamond’s aesthetic appearance, the higher the clarity grade. When determining the optimum clarity for a diamond, keep in mind that no diamond is entirely pure. However, the closer it gets to purity, the clearer it becomes. Diamonds with no or few inclusions are considered particularly rare and highly valued.
While clarity has a significant effect on the value of a diamond, most defects are invisible to the naked or unassisted eye.
Here are the different clarity grades to consider:
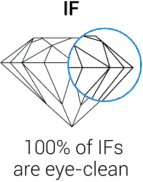
FL/IF
If you see anything on diamonds with a flawless clarity rating, it's most likely dust. If that small particle were an inclusion inside the diamond, it would undoubtedly reduce the stone to a VVS2.

VVS1
Only a strong microscope can reveal the pinpoints. At this magnification, VVS1 size inclusions are not visible. A standard picture, even enlarged, can only concentrate on a single degree of depth.

VVS2
A gemmological microscope is required to detect a VVS2 inclusion since the pattern is often composed of many smaller VVS1-sized spots that add up to a VVS2 clarity grade. Because the individual dots are too tiny to view with a jeweller’s loupe, they must be identified using a microscope.

VS1
Unlike VVS2 clarity inclusions, a VS1 never requires the use of a microscope. However, it's still tiny and will never be seen by just the human eye.

VS2
To the naked eye, VS2 clarity inclusions are nearly always clean.
Carat
Carat (ct.) refers to the unique unit of weight measurement used exclusively to weigh gemstones and diamonds. Carat weight is often confused with visual size even though it is a measurement of weight. You cannot actually see carat weight with the naked eye. Several factors affect the weight of a stone, such as density, the formulation of the jewel, and the shape.
A stone that is visually substantial does not indicate a high carat count. Depending on the shape and type of gemstone being weighed, the weight will visually show itself differently. For example, a 1.00 ct. round diamond will measure around 6.5mm, and a 1.00 ct. round sapphire will measure around 6.0mm. This is due to the varying density of different gemstones.
A phrase to look for when shopping is Total Carat Weight or TCW. Total carat weight represents the total weight of all diamonds or other gemstones in a piece of jewellery, when more than one stone is used.

Certification
A GIA Diamond is a diamond certified by the Gemmological Institute of America, the World’s foremost authority in independent third-party diamond certification. GIA diamonds are examined by a minimum of four highly trained diamond graders and gemmologists. At each step of a diamond’s evaluation, a more senior staff member independently grades the stone.
The GIA’s mission is to increase consumers’ trust in diamonds and Jewellery by upholding the highest standards of integrity, academics, science, and professionalism. They work toward this goal by providing jeweller and consumer education, conducting meticulous research, and developing state-of-the-art laboratory instruments for diamond inspections.
GIA diamonds are examined by a minimum of four highly trained diamond graders and gemmologists. At each step of a diamond’s evaluation, a more senior staff member independently grades the stone. To ensure impartial evaluations, the distribution of diamonds to graders is a completely random process.
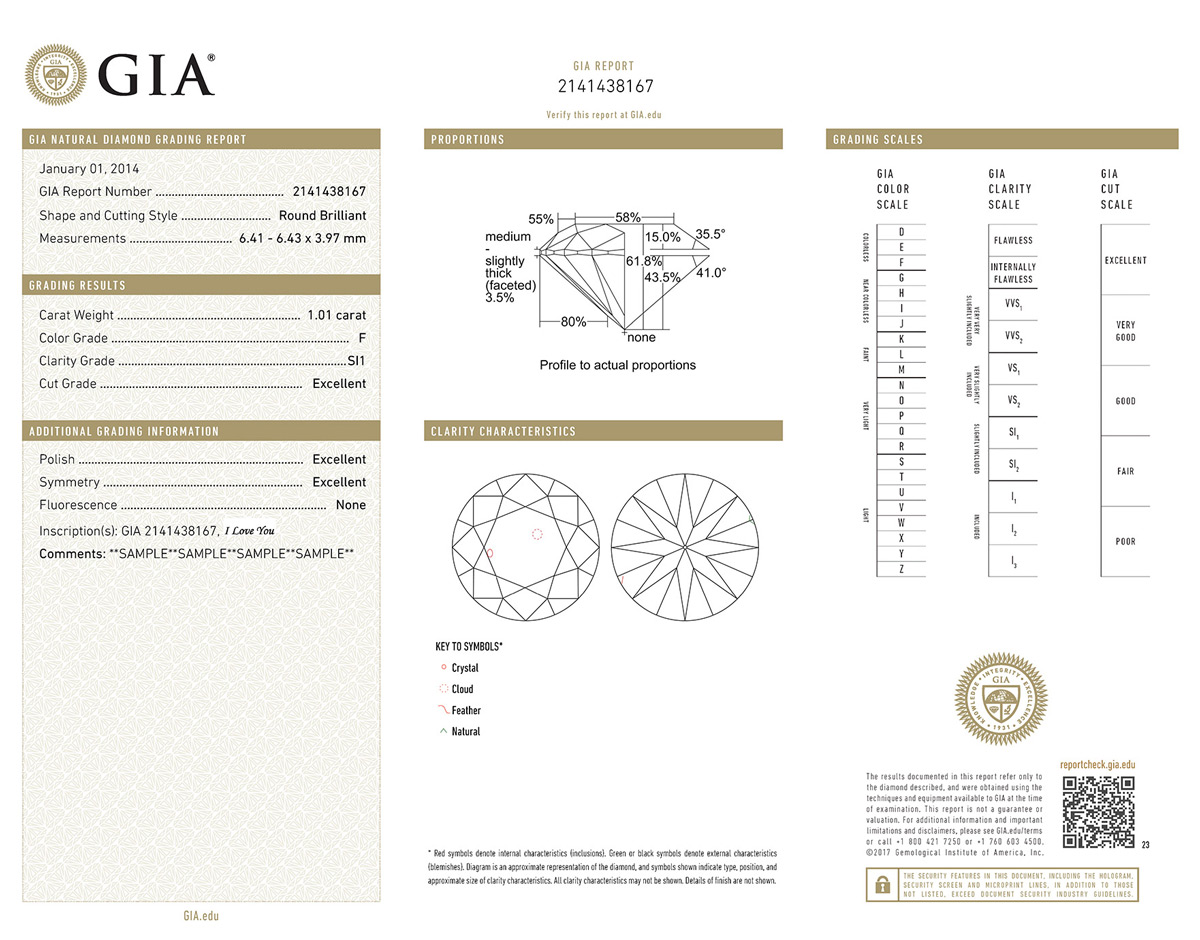
GIA Diamond Grading Report
The GIA Diamond Grading Report is issued for diamonds that fall in the D-Z colour range. This detailed report includes a full quality analysis of shape and cutting style, measurements, carat weight, colour grade, clarity grade, cut grade (for brilliant round-cut diamonds), polish and symmetry assessments, and fluorescence.
The report also includes a plotted diagram indicating the relative size and location of clarity characteristics, a proportion diagram, and GIA grading scales.
GIA Diamond Dossier Report
The GIA Diamond Dossier® is issued for diamonds between 0.15 and 1.99 carats that fall in the D-Z colour range.
This report includes all of the information featured in the Diamond Grading Report without a plotted diagram. All diamonds accompanied by a Diamond Dossier are laser inscribed and registered in the GIA inscription registry.
Fancy Coloured Diamonds
It’s no secret we at Gemaxis favour coloured gems above all, we made it our niche to display our work as colourful can be.
When it comes to Fancy Coloured Diamonds, Gemaxis Jewellery can offer you some of the rarest Diamonds available today.